- Find the interval of convergence (you must test endpoints, if applicable) of
the following series.
Solution:
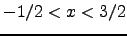
- Find a power series representation, and the interval on which it
represents the function, for
Solution:
 ,
, 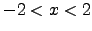
- Find the Taylor series centered at
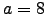 for
for
Solution:
- Using Taylor's Inequality, determine an upper bound for the error in approximating
 by its Taylor polynomial
by its Taylor polynomial  , centered at
, centered at 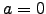 , on the interval
, on the interval
![$[-1/4,1/4]$](img40.png) .
.
Solution:

Timothy J Flaherty
2006-05-10

![]()

![]() ,
, ![]()
![\begin{displaymath}
f(x)=\sqrt[3]{x}
\end{displaymath}](img35.png)

![]()

![]()

![]() ,
, ![]()
![\begin{displaymath}
f(x)=\sqrt[3]{x}
\end{displaymath}](img35.png)

![]()