- Determine if the following sequence converges or diverges. If it
converges find the limit.
- Approximate the sum of the
following series to within
 using
using 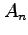 for the approximation via the integral test.
for the approximation via the integral test.
- Let

- Assuming that the sequence converges, find the limit.
- Prove, using mathematical induction, that the sequence is bounded.
- Prove, using mathematical induction, that the sequence is monotonic.
- Determine whether the sequence converges or diverges.
- Determine if the following series converges or diverges. If it converges
find the sum.
- Determine if the following series converges conditionally, converges
absolutely, or diverges.
- Determine if the following series converges or diverges.
- Determine if the following series converges conditionally, converges
absolutely, or diverges.
- Determine if the following series converges or diverges.
Timothy J Flaherty
2006-04-14













